Tax Alert - Reminder of changes to Vacant Residential Land Tax rules in Victoria from 1 January 2025
Reminder of changes to Vacant Residential Land Tax rules in Victoria from 1 January 2025
Background
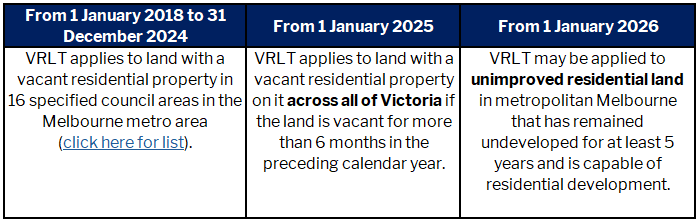
Vacant residential land tax (VRLT) may apply to residential land that is vacant for more than 6 months in the preceding calendar year (ie. from 1 January 2024 to 31 December 2024). Residential land can include:
- land with a home on it;
- land with a home which is being renovated or where a former home has been demolished and a new home is being constructed; or
- land with a home on it that has been uninhabitable for 2 years or more.
Residential land does not include land without a home on it (sometimes called unimproved land), commercial residential premises, residential care facilities, supported residential services or retirement villages.
The scope of what types of residential property will be exposed to the VRLT rules is being expanded over time, as follows:
The State Revenue Office (SRO) will release more information about unimproved land and VRLT in the short term.
The 6 month period of vacancy does not need to be continuous to trigger the VRLT rules.
VRLT rates & timing
For the year ending 31 December 2024, the VRLT rate is 1.0% of the capital improved value (CIV) of taxable land, which is the value of the land, buildings and any other capital improvements made to the property. The CIV is displayed on the council rates notice for the property.
Unlike land tax, there is no taxable value threshold for VRLT, which means land with a vacant residential property may be liable for VRLT regardless of its CIV.
From 1 January 2025, a progressive rate of VRLT will apply to non-exempt land with a vacant residential property and the rate is based on the number of consecutive calendar years the land has been liable for VRLT, as follows:
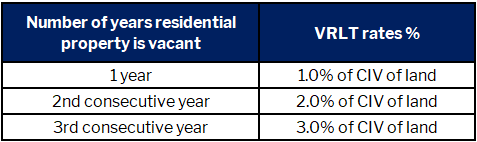
The use of the residential land in the calendar year ending 31 December 2024 will determine whether VRLT applies in 2025. For example, if land owned was vacant for more than 6 months during the calendar year ending 31 December 2024, the land owner must make a VRLT notification by 15 January 2025, and if any assessment is required it will be sent by the SRO during February 2025.
VRLT notifications
A land owner must lodge a VRLT notification via the SRO online portal (click here) by 15 January each year if:
- residential land is vacant for more than 6 months during the calendar year;
- the land is no longer vacant for more than 6 months during the calendar year;
- an exemption applies (discussed below); or
- an exemption ceases to apply/exemption changes.
If a land owner has made a VRLT notification in a previous year and circumstances have not changed, subsequent notification do not need to be made.
VRLT exemptions
If a property is exempt from land tax, it is also exempt from VRLT. In addition, there are four specific VRLT exemptions which apply to:
- holiday homes;
- apartments/homes/units used for work accommodation purposes;
- property transfers during the preceding year; and
- new residential land & newly developed properties where ownership is unchanged.
We will consider each exemption here and note any changes to the requirements from 1 January 2025.
VRLT exemption 1: Holiday homes
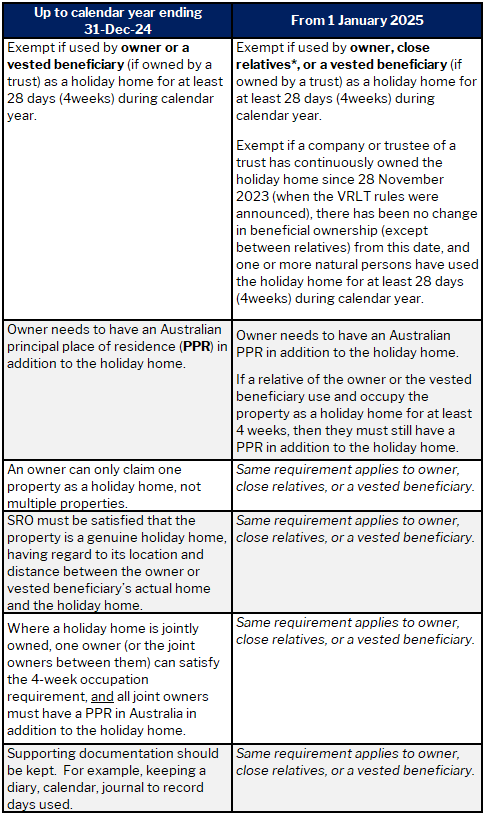
*A close relative of the owner includes a spouse or domestic partner, (grand) parents, (grand) children of owner/vested beneficiary or partner; brother, sister, niece or nephew of owner/vested beneficiary and their respective partners.
We note that use of the holiday home by friends (and not close relatives) does not count towards the 4-week occupation requirement from 1 January 2025.
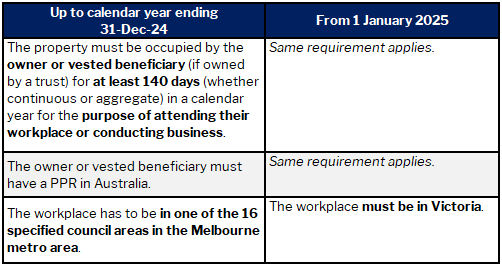
VRLT exemption 2: Work accommodation
The work accommodation exemption applies to circumstances where someone may live in regional Victoria or another state or territory and maintain an apartment/townhouse to stay in while they work away from their usual home.
VRLT exemption 3: Property transfers during the preceding year
Properties that change ownership during a calendar year are exempt from VRLT in the following year.
The change of ownership must occur during the calendar year. It is not sufficient that the property is available for sale or awaiting settlement as at 31 December of the year preceding the tax year. Importantly settlement must take place no later than 31 December.
This exemption remains unchanged after 1 January 2025.
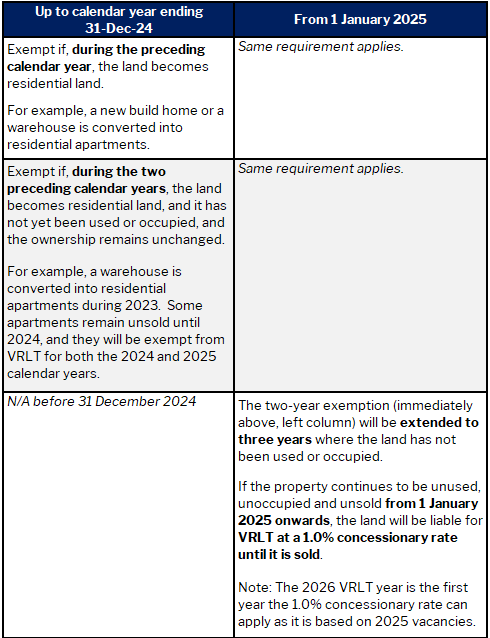
VRLT exemptions 4: New residential land & newly developed properties where ownership is unchanged
Please do not hesitate to contact your Lowe Lippmann Relationship Partner if you wish to discuss any of these matters further.
Liability limited by a scheme approved under Professional Standards Legislation